plotting in Python with Seaborn: Joint plot
Introduction
In Visualization with Seaborn of this series, we were introduced on the power visualization and dove into distributions plot. In this post we are going focus on jointplot. jointplot is used to plot the histogram distribution of two columns, one on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. A scatter plot is by default drawn for the points in the two columns. Seaborn has nifty function called jointplot(), which is dedicated for this type of plot.
Loading libraries
Though most people are familiar with plotting using matplot, as it inherited most of the functions from MatLab. Python has an extremely nady library for data visualiztion called seaborn. The Seaborn library is based on the Matplotlib library. Therefore, you will also need to import the Matplotlib library.
Dataset
We are going to use a penguin dataset from palmerpenguins package (Horst, Hill, and Gorman 2020). We do not need to download this dataset as it comes with the seaborn package. We only need to load it from the package into our session using sns.load_dataset function and specify the penguins as the name of the dataset and assign it as df;
species island bill_length_mm ... body_mass_g sex year
0 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 ... 3750 male 2007
1 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 ... 3800 female 2007
2 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 ... 3250 female 2007
3 Adelie Torgersen NaN ... -2147483648 NaN 2007
4 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 ... 3450 female 2007
[5 rows x 8 columns]A printed df dataset shows that is made up of various measurements of three different penguin species — Adelie, Gentoo, and Chinstrap. The dataset contains seven variables – species, island, bill_length_mm, bill_depth_mm, flipper_length_mm, body_mass_g, sex, and year.
The joint plot is used to plot the histogram distribution of two columns, one on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. A scatter plot is by default drawn for the points in the two columns. To plot a joint plot, you need to call the jointplot() function. The following script plots a joint plot for bill_length_mm and bill_depth_mm columns of the df dataset.
<seaborn.axisgrid.JointGrid object at 0x000000005A814D00>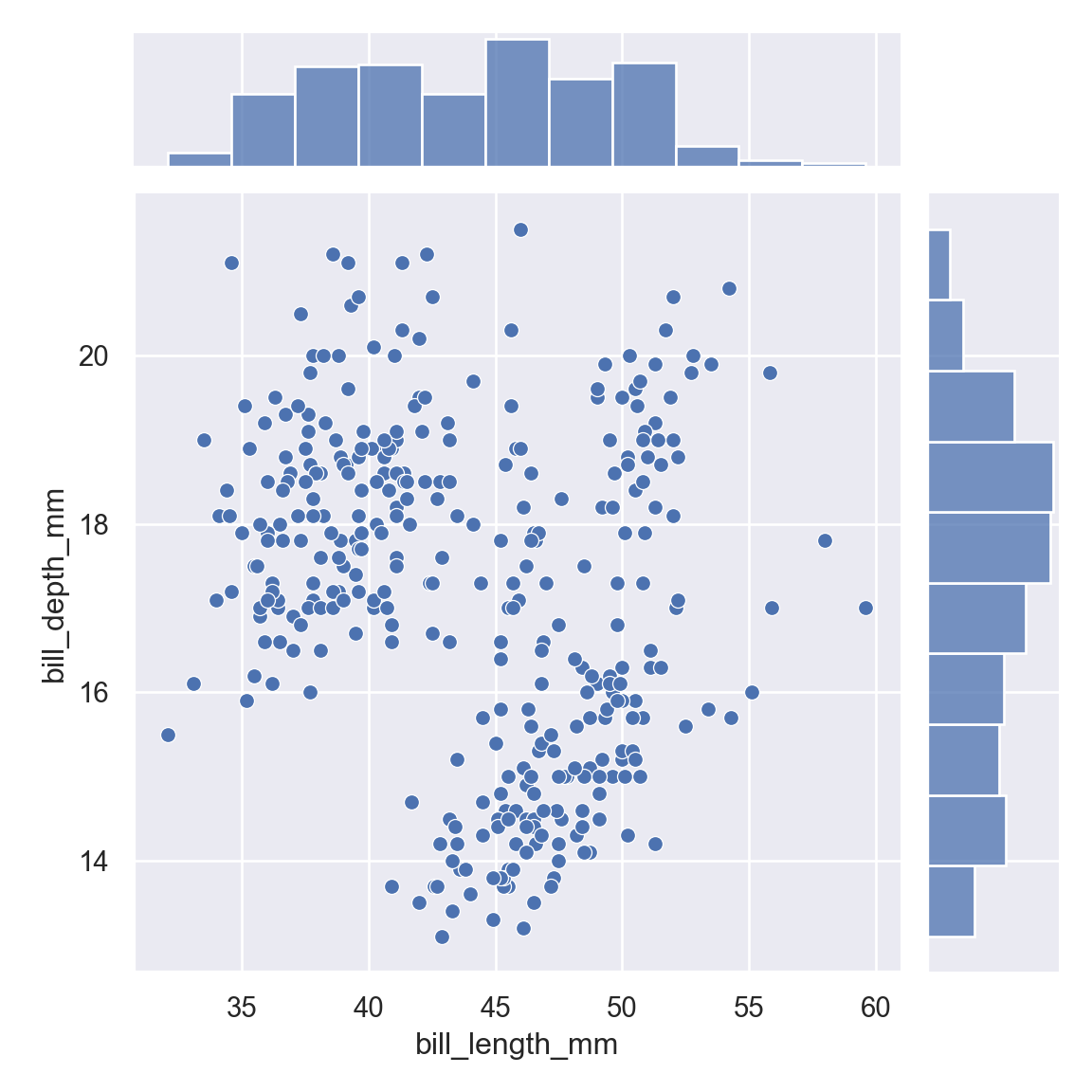
Assigning a hue variable will add conditional colors to the scatter plot and draw separate density curves (using kdeplot()) on the marginal axes. In this case we specify hue = "island"
<seaborn.axisgrid.JointGrid object at 0x000000005D55D160>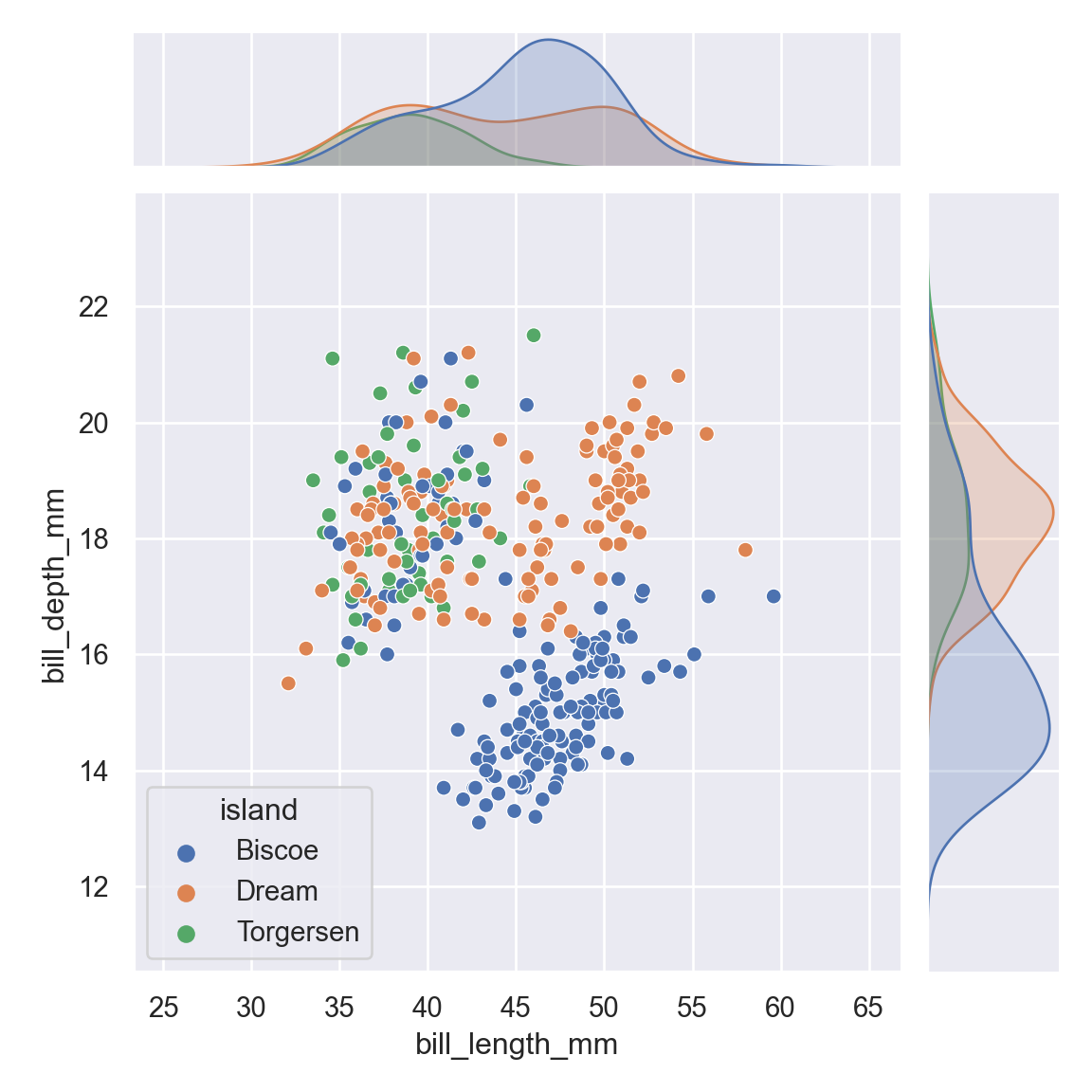
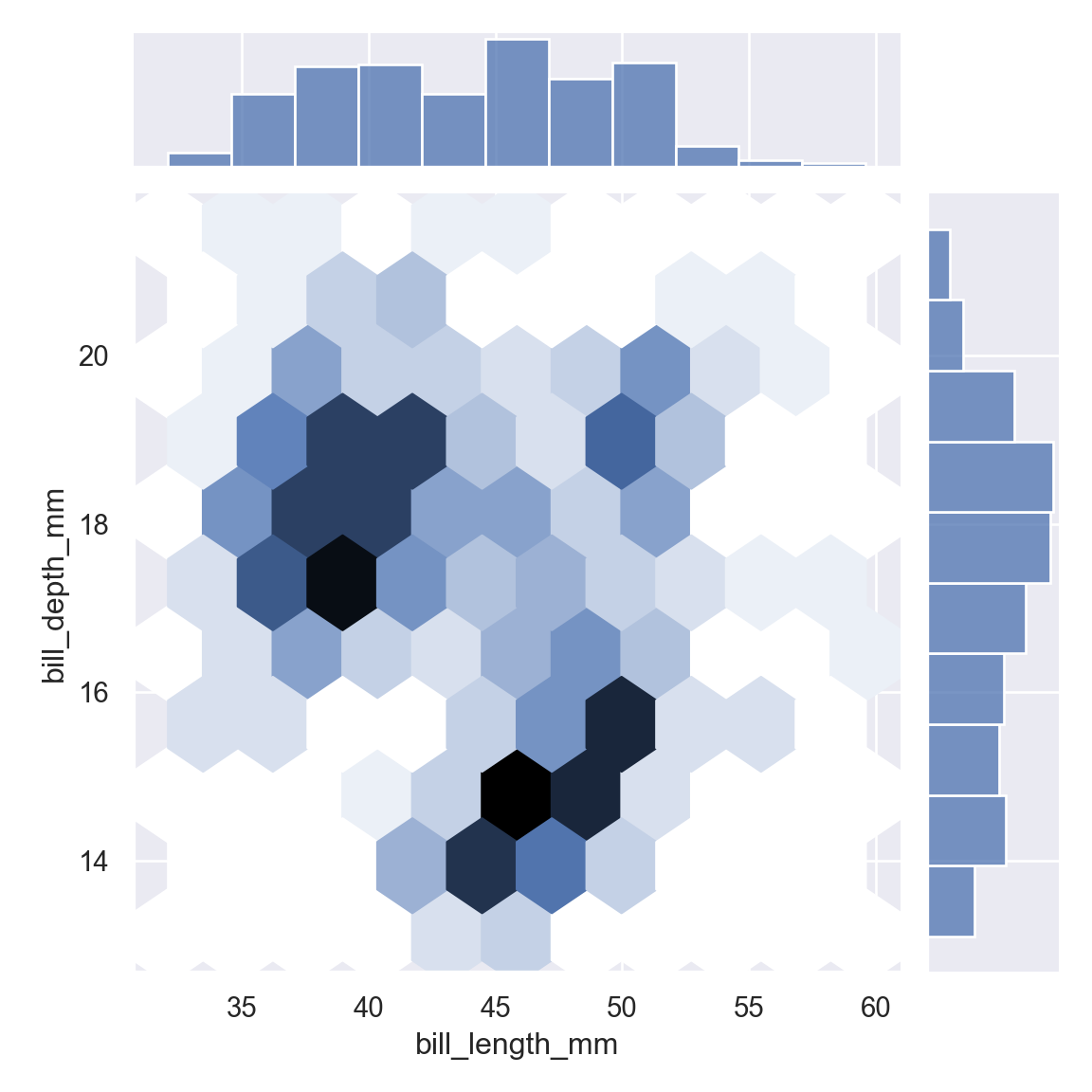
Several different approaches to plotting are available through the kind parameter. Setting kind=“kde” will draw both bivariate and univariate KDEs:
fig = plt.figure()
sns.jointplot(data=df, x="bill_length_mm", y="bill_depth_mm", hue="species", kind="kde")<seaborn.axisgrid.JointGrid object at 0x000000005D707310>
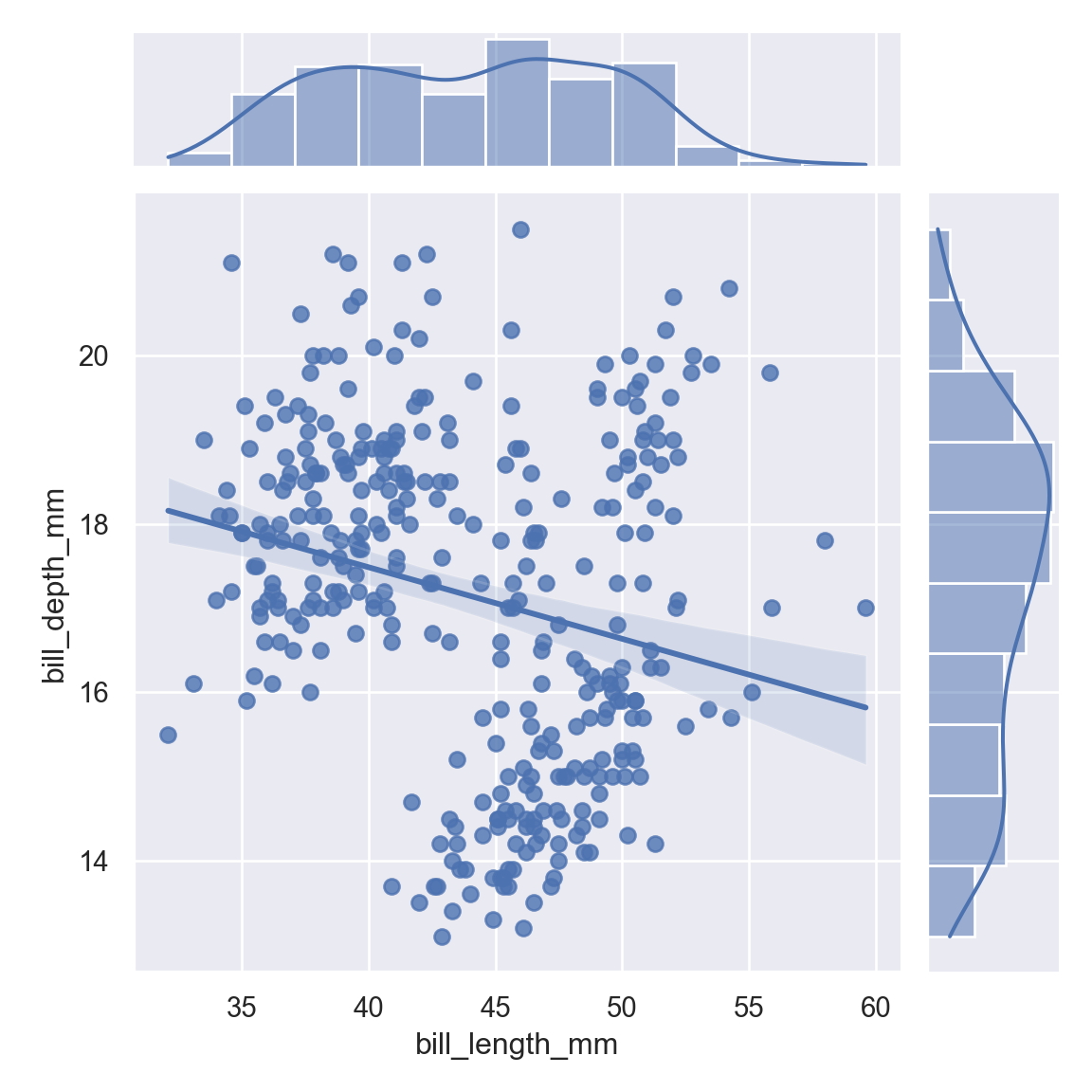
Set kind="reg" to add a linear regression fit (using regplot()) and univariate KDE curves:
<seaborn.axisgrid.JointGrid object at 0x000000005D8163D0>